Level 4 Communication Skills: Good communication skills are necessary to effectively explain complex data findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Food for Thought 1:
It is important to mention that ChatGPT-4 AI did not describe the most important Level of Attention ("Level 6 - Moral and Ethical aspects of Data Analysis").
Food for Thought 2:
Also the fact that ChatGPT-4 AI is able describe complex learning mechanisms and levels of attention implies that ChatGPT-4 AI is not just "Stochastic Parrot" - (Geoffrey Hinton & Yann LeCun) but it does "understand" the real world. (Geoffrey Hinton).
-------------------------------------------------------------
ChatGPT-4 : What are moral and ethical aspects of Data Science?
-
Abraham Maslow – Hierarchy of Needs
-Health Conditions
Wellness
Tools
Featured
Connect
A (Realistic) Guide to Becoming Self-Actualized
Definition
Pyramid of needs
What it isn't
Characteristics
How to achieve it
Things to keep in mind
Takeaway
What does it even mean?
Self-actualization can mean a lot of things depending who you ask.
One of the most broadly accepted definitions comes from Abraham Maslow, a humanistic psychologist. He described self-actualization as the process of becoming “everything you are capable of becoming.”
Kim Egel, a San Diego therapist, similarly explains it as the “ability to become the best version of yourself.”
It all sounds great — but how do you actually become this best version of yourself? And how will you know you’ve achieved it?
“There’s no script for that,” Egel adds. “Everyone has to find their own unique ways to hear the inner wisdom that can help them live a life of truth.”
Only you can determine what self-actualization means for you, but we’ve got the info to help you get the ball rolling and make the process feel less daunting.
First, a note about Maslow’s pyramid
A lot of discussions about self-actualization refer to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. He theorized that people need to satisfy four basic types of needs before they can satisfy a fifth need for self-actualization.
He organized these needs into a pyramid:
The lowest stage contains the most basic needs, such as food, water, and shelter.
The second stage represents safety needs.
The third includes belonging or relationship needs.
The fourth stage involves respect or esteem needs, both from the self and others.
The fifth stage, or the tip of the pyramid, is self-actualization.
While this pyramid model can provide some general guidance on the path toward self-actualization, it has some limitations. For example, plenty of people lack adequate food and shelter while still enjoying and maintaining strong relationships and respecting others.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a good thing to be aware of as you explore self-actualization, but it’s not the only way to approach things.
What self-actualization isn’t
Again, self-actualization can mean a lot of things to different people. To cut through some of the ambiguity, it might be helpful to think about what self-actualization isn’t.
Self-actualization doesn’t involve perfection or things always going smoothly. You can become self-actualized and still face difficulties.
In fact, a huge part of self-actualization is recognizing your limits in addition to focusing on your unique strengths — whether those involve practical skills, parenting, artistic talents, or emotional insights.
From there, you would live your life in a way that best utilizes your strengths while taking steps to achieve your dreams, both large and small.
For example, say you dream of becoming a pop singer. You love music, but can’t really carry a tune. Eventually, you find that you’re pretty good at playing the guitar and making music that way.
You practice, develop this skill, and continue improving over time. Maybe you never become a pop singer, but you live out your need to make music in a different way.
What it looks like
Now that we’ve identified a basic definition of what self-actualization is (and isn’t), it’s time to get into the nitty-gritty of what it truly means to be the best version of yourself.
There are a range of characteristics that tend to be associated with self-actualization.
Keep in mind that it’s possible to achieve it without meeting every characteristic, just as it’s equally possible to have these traits before reaching the point of self-actualization.
Generally speaking, self-actualized people:
Live independently. They don’t structure their lives around the opinions of others. They may not seem swayed by social feedback. They also have an appreciation for solitude and don’t always need company.
Have a sense for reality and truth. They may seem more grounded and in touch with actual possibilities and have an easier time detecting falseness from other people.
Are comfortable with the unknown. They don’t mind not knowing what the future holds.
Have compassion, kindness, and acceptance. This goes both for themselves and for others they encounter.
Have a good-natured sense of humor. They can laugh at themselves when they make mistakes and help others see humor in challenging situations.
Enjoy meaningful friendships. They tend to build long-lasting relationships with a few people instead of casual friendships with many people.
Have a sense of spontaneity. They live more naturally, rather than in a rigid way, and aren’t afraid to follow what happens in the moment instead of sticking to routine.
Are creative. Creativity doesn’t just refer to artistic abilities. Some self-actualized people might have a knack for looking at problems in new ways of thinking along different lines than other people do. They may simply lack inhibition, another characteristic of a spontaneous nature.
Enjoy peak experiences. A peak experience describes a moment of euphoria, wonder, and joy, often characterized by a sense of feeling connected to the universe. They might seem like eye-opening moments, where deeper meanings suddenly become clear. They aren’t necessarily spiritual, though.
Focus on things bigger than themselves. They tend to see the big picture instead of only considering their own lives, and may dedicate their lives to a mission, cause, or deeper purpose.
Stop and smell the roses. They appreciate each positive or joyful moment — a sunrise, a partner’s kiss, a child’s laugh — as if it were the first, no matter how many times they’ve already experienced it.
Have a sense of justice. They have compassion and care for all people, and work to prevent acts of injustice or unethical behavior.
Possess Gemeinschaftsgefühl, or “social feeling.” This word, coined by Alfred Adler, describes an interest and concern for the general well-being of other humans.
If all of this feels unattainable, remember that self-actualization is a process, not an endgame. There’s no single point where you “should” end up on the journey.
“From a therapist’s perspective, self-actualization is a constant work in progress,” Egel says. “In our humanness, we are never going to stay completely the same.”
How to work toward it
Self-actualization is an admirable goal to work toward. If you live your life with purpose and authenticity and show concern for others, you’re headed down the right track.
These tips can serve as additional guideposts along your way.
Practice acceptance
Learning to accept what comes — as it comes — can help you achieve self-actualization.
This might mean you work with situations as they turn out — such as a rainy day when you planned an outdoor event — rather than wishing things had happened in a different way.
It could also mean you get more comfortable accepting unknowns in your life. Or, maybe it means you try to avoid wishful thinking and look at things in more realistic ways.
Acceptance also refers to human experience. It’s not always easy to like people who behave in unkind or problematic ways. You can, however, still extend compassion by recognizing that everyone has their own circumstances to deal with.
Remember: Accepting someone doesn’t mean you have to spend your time with them.
Live spontaneously
To live with spontaneity, try enjoying each moment as it comes, without trying to worry about what you should do.
It might feel easy and safe to stick with what you know, but fight that urge. Take chances (within reason) and be open to trying new things.
Thinking back to your younger years can help you tap into your inner spontaneity. Maybe you used to roll down hills instead of walking along the footpath. Or you threw an impromptu picnic in the backyard, because why not?
Spontaneity can be as simple as taking a different route home or trying a food you’d never considered before. Your heart can be a great guide, so pay attention to any gut instincts you feel.
Get comfortable with your own company
Your relationships with friends, family, and romantic partners play an important part in your life. But it’s just as important to nurture your relationship with yourself.
Pretty much everyone benefits from some occasional “me time.” Some people may need more or less than others. How you spend this time may matter less than what you get from it.
Self-actualized people typically feel calm and at peace on their own, so aim to reconnect with yourself until you look forward to your moments alone as much as (or more than) the time you spend with others.
Appreciate the small things in life
This sounds like a cliche, but it’s a key step to self-actualization. Take time to appreciate aspects of your day-to-day life that often go ignored in the busyness of living.
Think of things like:
a delicious meal
cuddles from your pet
good weather
a job you enjoy
Live authentically
This phrase gets thrown around a lot, but what does it really mean? Living authentically involves honoring your truth and avoiding things like dishonesty, manipulation, or denial of your needs.
This might mean worrying less about what other people think of you.
Instead of living according to what other people say or suggest you should do, you follow insight gained from personal experience and live according to the guidance of your heart.
You’re also honest with yourself about your needs and desires. You respect the rights and needs of others, of course, but you work to achieve your goals as only you can. You work to maximize your potential, not someone else’s.
Develop compassion
Self-actualized people have deep feeling for other living creatures. Their compassion extends beyond their immediate social circle and those they know in their daily life to humanity and the world as a whole.
Compassion comes more easily to some people than others.
If you struggle to understand and empathize with people who are very different than you, try learning more about people who have different life experiences through reading books or consuming other media produced by people from a different background.
Looking for more ways to build compassion? Try:
volunteering for charitable organizations or human interest projects
exploring ways to improve your community
calculating your carbon footprint and taking steps to make improvements
Talk to a therapist
Therapy can help you take steps toward any of your goals, and self-actualization is no exception. Plus, you don’t need to be facing a mental health issue to seek therapy.
Wanting to develop compassion, spontaneity, and authenticity are totally acceptable reasons to seek therapy.
In therapy, you can also learn more about self-actualization in general terms, since the concept can be a difficult one to grasp.
Talk therapy, which most people just call “therapy,” is actually one type of humanistic therapy (which Maslow helped develop).
If you’d like to dig a little deeper into spirituality or existential topics, though, consider exploring more specialized approaches like transpersonal therapy or existential therapy.
Bezzy Resource
Depression Is Not Just ‘In Your Head': 7 Physical Symptoms
We don’t always pair depression with physical pain but research shows depression can really hurt. Depression can cause body aches, stomach pain, and more.
READ MORE
Things to keep in mind
Committing to the process of becoming self-actualized can feel overwhelming. Try not to get too caught up in doing all the “right” things or holding yourself to impossibly high standards.
For what it’s worth, Maslow believed true self-actualization was fairly rare. Egel agrees, asking, “How many people do you know who are living their life 100 percent true to themselves?”
Plus, past challenges or present life circumstances can make things like growth, self-reflection, and authenticity more difficult.
Finally, know that even the most self-actualized people still have room to grow.
“Growth never ends until the journey of life is complete,” Egel says. “Reaching a point of self-actualization has to be maintained, just as a level of peak fitness must be maintained by consistent healthy habits and behaviors.”
Recognizing this need for continued growth is also — you guessed it — part of self-actualization.
The bottom line
Self-actualization isn’t a one-size-fits-all goal. No two people are exactly alike, so everyone will probably have a slightly different path.
It’s also not something you can accomplish in a weekend.
True self-actualization may be more of a long-term (even lifetime) goal than a quick road to self-improvement. That said, working to maximize your potential and become your best self is a great way to lead a more fulfilling life.
So, while self-actualization might seem somewhat overwhelming, don’t let that stop you. Take each day as it comes and keep an open mind.
________________________________
Feb 27, 2020
Written By
Crystal Raypole
Edited By
Kelly Morrell
Medically Reviewed By
Timothy J. Legg, PhD, PsyD
Copy Edited By
Jamie Elmer
Medically reviewed by Timothy J. Legg, PhD, PsyD — Written by Crystal Raypole on February 27, 2020
HEALTHLINE NEWSLETTER
Abraham Maslow – Hierarchy of Needs
More information:
Domenico Di Sante et al,
Deep Learning the Functional Renormalization Group,
Physical Review Letters (2022).
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.136402
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Among his concerns:
- Generated media could erode the average person’s ability to gauge reality.
- AI models could cause massive unemployment by automating rote work, and perhaps not-so-rote work.
- Automated code generators eventually could write programs that put humans at risk.
- Hinton supports global regulation of AI but worries that it would be ineffective. Scientists probably can devise more effective safeguards than regulators, he said.
Nvidia CEO predicts the death of coding — Jensen Huang says AI (and developers of AI) will do the work, so kids don't need to learn coding (from layer 2 to layer 5 when coding can be automated using Generative AI coding assist tools)
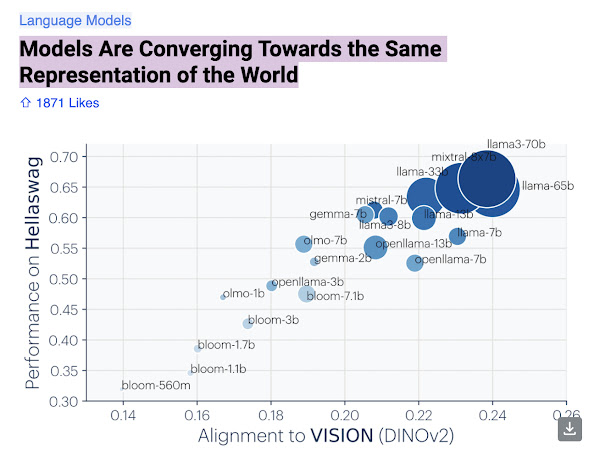
AI Models Are Converging Towards the Same Representation of the World.
### Technical Skills:
1. **Programming Languages:**
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python and R is crucial. These languages are commonly used for data manipulation, analysis, and building machine learning models.
2. **Statistical Analysis:**
- A solid understanding of statistics, including hypothesis testing, probability distributions, and regression analysis, is essential for interpreting data and making informed decisions.
3. **Data Manipulation and Cleaning:**
- Skills in data wrangling, cleaning, and preprocessing using tools like Pandas (Python) or dplyr (R) are important for preparing data for analysis.
4. **Machine Learning:**
- Knowledge of machine learning algorithms and techniques, such as classification, regression, clustering, and deep learning, is necessary for predictive modeling.
5. **Data Visualization:**
- Proficiency in data visualization tools and libraries, such as Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau, or Power BI, is important for presenting insights in a clear and understandable manner.
6. **Database Management:**
- Experience with SQL and NoSQL databases, as well as data extraction and querying, is important for managing and accessing large datasets.
7. **Big Data Technologies:**
- Familiarity with big data technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and distributed computing frameworks can be beneficial for working with large-scale data.
### Analytical Skills:
1. **Critical Thinking:**
- The ability to approach problems logically and analytically, identifying patterns and drawing meaningful conclusions from data.
2. **Problem-Solving:**
- Strong problem-solving skills to develop innovative solutions and strategies based on data insights.
3. **Domain Knowledge:**
- Understanding the specific industry or domain in which you are working can help in contextualizing data insights and making relevant recommendations.
### Soft Skills:
1. **Communication:**
- Effective communication skills to explain complex data insights to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate with cross-functional teams.
2. **Curiosity and Continuous Learning:**
- A natural curiosity and willingness to stay updated with the latest trends, tools, and techniques in data science.
3. **Teamwork:**
- The ability to work well in teams, as data science projects often involve collaboration with other data scientists, engineers, and business professionals.
4. **Attention to Detail:**
- Precision and attention to detail are important for ensuring data accuracy and integrity.
### Project Management Skills:
1. **Time Management:**
- The ability to manage time effectively, prioritize tasks, and meet deadlines.
2. **Project Planning:**
- Skills in planning and executing data science projects, including defining objectives, milestones, and deliverables.
Developing a combination of these skills can help you become a well-rounded data scientist capable of tackling complex data challenges and making impactful decisions.
### 1. **Customer Support and Chatbots:**
- **Automated Customer Service:** LLMs can power chatbots that handle customer inquiries, provide support, and resolve issues efficiently.
- **Live Chat Assistance:** They can assist human agents by suggesting responses and providing relevant information during live chat sessions.
### 2. **Content Creation:**
- **Writing and Editing:** LLMs can generate articles, blog posts, reports, and other types of content. They can also assist with editing and proofreading.
- **Creative Writing:** These models can help in writing stories, poems, and scripts, providing inspiration or even drafting entire pieces.
### 3. **Education and E-Learning:**
- **Tutoring:** LLMs can act as virtual tutors, helping students understand complex concepts, answering questions, and providing explanations.
- **Content Generation:** They can create educational materials, quizzes, and summaries of academic content.
### 4. **Healthcare:**
- **Medical Documentation:** Assisting in drafting medical reports, patient summaries, and other documentation.
- **Patient Interaction:** Providing preliminary consultations, answering patient queries, and delivering health information.
### 5. **Business and Finance:**
- **Market Analysis and Reports:** Generating financial reports, market analysis, and business insights based on data.
- **Customer Interaction:** Assisting in customer relationship management by generating personalized responses and communications.
### 6. **Software Development:**
- **Code Generation and Assistance:** Helping developers by generating code snippets, providing documentation, and debugging code.
- **Documentation:** Creating and maintaining technical documentation and user manuals.
### 7. **Translation and Localization:**
- **Language Translation:** Providing real-time translation services for text and speech.
- **Localization:** Adapting content to different cultures and languages, ensuring it resonates with local audiences.
### 8. **Research and Development:**
- **Literature Review:** Summarizing and synthesizing research papers and articles.
- **Hypothesis Generation:** Assisting in formulating research hypotheses and experimental designs.
### 9. **Entertainment:**
- **Gaming:** Creating dialogues, narratives, and interactive stories for video games.
- **Interactive Experiences:** Developing virtual assistants and characters for immersive experiences in VR and AR environments.
### 10. **Legal and Compliance:**
- **Document Review:** Analyzing legal documents, contracts, and compliance reports.
- **Legal Research:** Assisting in legal research by summarizing case laws and legal precedents.
### 11. **Personal Productivity:**
- **Virtual Assistants:** Enhancing virtual personal assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa) to provide more natural and context-aware interactions.
- **Task Management:** Assisting with scheduling, reminders, and task organization.
### 12. **Marketing and Sales:**
- **Copywriting:** Creating persuasive marketing copy, product descriptions, and ad content.
- **Customer Insights:** Analyzing customer feedback and sentiment to inform marketing strategies.
### 13. **Social Media Management:**
- **Content Scheduling and Creation:** Generating posts, captions, and managing social media calendars.
- **Engagement:** Interacting with followers and responding to comments and messages.
### 14. **Data Analysis:**
- **Data Summarization:** Summarizing large datasets and generating reports.
- **Natural Language Querying:** Allowing users to query databases using natural language.
### 15. **Accessibility:**
- **Assistive Technologies:** Enhancing tools for individuals with disabilities, such as voice-to-text applications and screen readers.
The versatility and adaptability of LLMs make them a powerful tool in transforming various aspects of both personal and professional life. However, it’s essential to consider ethical implications and ensure responsible use of these models to avoid misuse and mitigate potential biases.





No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.